Welcome to IAK Library
Ancient Civilizations
Tracing the Foundations of Human Civilization
An overview of the four great ancient civilizations that shaped human history.
We are one Family.
“青山一道同云雨,明月何曾是两乡。”
The Four Oldest Ancient civilizations:
-
Mesopotamia (Babylon):Tigris River, Euphrates River
-
Egypt
-
Indus valley
-
China
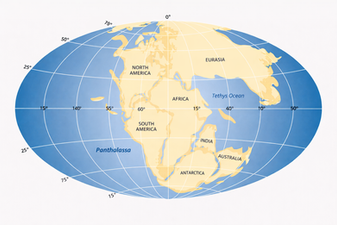
Pangaea:335 million years ago
“Classic of Mountains and Seas” 《山海经》
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiː.ə/) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists.



Wisdom & Reflection
The study of ancient civilizations is not about nostalgia, but about rediscovering the roots of human culture.
Their innovations in writing, law, religion, and urban life invite us to reflect on how societies rise, transform, and endure — offering timeless wisdom for the challenges of our modern world.